Charging of a capacitor
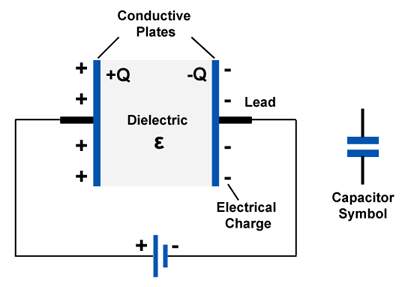
A capacitor is one of the electric components of an electrical circuit or network. A capacitor is a storing device that stores electrical current or voltage in plates. A capacitor is consists of two parallel conducting plates carrying charges of equal magnitude but in opposite directions, separated by a dielectric medium.
When voltage is supplied by an electric source to a capacitor, it stores voltage. A capacitor stores voltage until supplied voltage becomes equal to capacitor voltage. Capacitors are used in electrical network circuits to charge the circuit. Capacitors can be used instead of batteries to charge a circuit or as voltage suppliers.

The charging of a capacitor depends upon the material of conductor plates, the strength of the dielectric medium between plates, and some other factors. Each material as dielectric has a different strength of charging the capacitors. The capacity of charging is inversely proportional to the distance between the plates, as distance decreases between plates, the strength of the capacitor to store more charges increases, and vice versa.
Where the area between plates is directly proportional to the capacitance of the capacitor, as area increases capacity increases. When Capacitor is charged, it can work like a battery to supply voltage to the circuit. While a capacitor is charging by voltage supply, the current is initially high but, decreasing by time as the capacitor is fully charged.
The capacitance of the capacitor has an inverse relation to the frequency of the voltage source.
The capacitance of the capacitor is the ratio of the charge on the plate and the potential difference between plates.
The S.I unit of capacitance is farad and often picofarad and microfarad are used for the capacitance of the capacitor.
The charge on the capacitor 'Q' is linearly proportional to the potential difference 'V' in the conducting plates of the capacitor.
Q~V, Q = CV or C = Q/V
The dielectric medium is capable of supporting the electrostatic forces.
The procedure of charging the capacitor is as the following way.
When the capacitor is connected to the battery, electrons on the left plate in the capacitor are attracted by the positive terminal of the battery and then moves to a right side plate.
There is an excess of positively charged holes on the left side and an excess of negatively charged electrons.
Capacitors are used in communication apparatus such as VCRs, radios, television, radar, etc. These are can be adjusted by tuning controls. There are a lot of appliances and electronic devices in which capacitors are used such as energy-storing devices and more.



No comments:
Post a Comment