Hi, welcome to an electric tech. Here are interesting and amazing facts and information about electrical technology. Now the world has become full of different technologies and electrical is one of them. you will be able to find informative topics, short facts and more about electrical technology. Let's start a new interesting journey in electrical technology.
Self inductance of a solenoid
Mutual induction principle
Mutual induction
 |
| Mutual induction between two coils |
 |
| Mutual induction |
 |
| Emf induces in the second coil when a change in flux in the first coil link to another coil |
How does an electric generator work
How does an electric generator work?
What's alternating current
What's the alternating current
Current is the flow of electrical charges or electrons in a specific path. When voltage is supplied to a circuit, electric device, the current starts to flow. There are two types of electric current; alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). These are free electrons in the material that cause to flow and produce current. An alternating current is a current in which periodically reverses its direction and changes its magnitude with time. The polarities and direction of AC quantities like current and voltages change over time. Whereas direct currents(DC) are unidirectional. It depends upon the supplied voltage that generates DC or AC. Alternating current follows in the sinusoidal waveform. Alternating voltage produces alternating current in the electrical device or circuit. Alternating current is more dangerous than direct current. Ac quantity follows a sine wave with a change in its magnitude over time. Alternating current is easy in the transmission of current through long distances. There are two directions in a sine wave. Upperside is a positive one and lower is negative.
 |
| The sinusoidal waveform of alternating current |
The direction of alternating current alternates with the time as a sine wave. Whereas the direction of direct current dc is constant during the time. The Alternating current behaves like a wave, the sinusoidal wave is generated by alternating current and voltage. In AC, there is the peak value, RMS value, and some other values that are considered and evaluated in ac quantities. The basic source of dc is the battery but, ac power is distributed and transmitted to residences and businesses.
Alternating current is used in our home, office, and other places. Almost all our appliances like television, kitchen appliances, fans, and other electrical devices that we use in our daily life operate on alternating currents. Audio and radio signals in electrical wires operate on alternating currents.
Electrical motor and generator can not operate on dc supply, so these are supplied and operated by AC for generating rotation in the coil or shaft. Similarly, in the transformer for transferring electric power from one circuit to another ac power is supplied due to which alternating current is produced in coils of the transformer. The frequency of ac quantity varies time by time. Electrical motors, generators, transformers, and many electrical machines operate on alternating currents and provide us efficient work. In alternating current, there are fewer losses in power than direct current so it is convenient for us and we use it as electricity for transmitting over long distances.
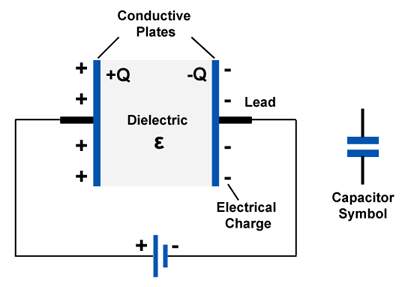
Charging of a capacitor
Charging of a capacitor

Electromegnatic induction
Electromagnetic induction
Whenever a coil of wire is brought to a static magnetic field or a stationary coil linked to the varying magnetic field, a change in the magnetic flux produces induced emf.
Electrical current can be generated through a change in magnetic flux in a varying magnetic field.
 |
| The process of electromagnetic induction |
Faraday's law of the electromagnetic induction
An English scientist Micheal Faraday gave the law of electromagnetic induction.
Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction states, "an emf or voltage is induced when the magnetic flux changes with time linked to the coil".
The rate of change of magnetic flux, emf will be induced
induced emf = - d/dt magnetic flux
Minus sign shows the Lenz's law
Lenz's law shows the direction of the induced field. The induced voltage or emf is in the opposite direction to flux.
Fleming's right rule is used for the direction of emf, the motion of the conductor, and the magnetic field.
Electromagnetic induction is used to power electrical devices such as electric motors, generators and transformers, and more.
The source of electromagnetism is the electric current flowing through a coil of wire.
 |
| Emf induces when there is relative motion between coil and permanent magnet |
Uses
It is used in electrical devices such as electrical generators(hydroelectric dams), electric motors, transformers, etc
Where mechanical power is used to move the magnetic field to generate a voltage
Induction motors, current lamp
Loudspeaker, headphones
Magnetic data storing devices VCR, recording tape, hard disk, and more
Electric bells, transformers, and
The advantages of electromagnetic induction are:
Electrical power(AC or DC) can be generated by using electromagnetic power sources.
There is no need for external electrical sources to produce electrical power.
Working principle of transformer and applications
Working principle and function of transformer
 |
| Transformer |
Applications
- To Regulate alternating current,
- To start and stop the flow of electricity
- Battery charging
- Steel manufacturing
- Transmission and distribution lines
- Transformers are used to set apart two circuits electrically and it is used to increase or decrease alternating voltage without changing power in appliances
- It is also used in power generation and distribution of power and, in high-power industrial loads such as motor drives and other appliances.
- The transformer is also used at the power stations and grid stations through which voltages are supplied to industrial and residential areas.
How does an electric motor work
How does an electric motor work
What is an electric motor?
 |
| Electrical motor |
How does an electric motor work
 |
| The working function of an electric motor |
Construction of a basic electric motor
 |
| Structure of electric motor |
Applications of electric motor
- The electric motor is used in water pumps, drill machines, industrial equipment.
- There are different machine tools, power tools, fans, compressors, rolling mills, and turbines.
- Spinning machines, lifts, centrifugal pumps
PN junction diode and its applications
PN junction diode
A PN junction is an interface between two types of semiconductor material, p-type and n-type. The "p" (positive) side contains an excess of holes while the "n" (negative) side contains an excess of electrons in the outer shells of the electrically neutral atoms there. This allows electrical current to pass through the junction only in one direction. The p-n junction is created by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy. If two separate pieces of material were used, this would introduce a between the semiconductors that would severely inhibit its utility by scattering the electrons and holes. P-N junctions are the elementary building blocks of semiconductor electronic devices such as diodes, transistors, solar cells, and integrated circuits. They are the active sites where the electronic actions of devices take place.
 |
| PN junction diode |
Forward biased
When the p-type is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and the n-type to the negative terminal then the p-n junction is said to be forward-biased. In the case of the forward-biased junction, the built-in electric field at the p-n junction and the applied electric field are in opposite directions. When both the electric fields add up, the resultant electric field has a lower magnitude than the built-in electric field. The potential barrier is almost eliminated and the current starts flowing in the circuit. results in a less resistive and narrow depletion layer or region. The depletion region’s resistance becomes negligible when the applied voltage is large.
Reverse biased
Application of a junction diode
- PN junction diode can be used as a photodiode as the diode is sensitive to the light when the configuration of the diode is reverse-biased.
- It is used as a rectifier in many electric circuits and as a voltage-controlled oscillator in varactors.
- It can be used as a solar cell and used in switches digital design.
- The forward-biased diode is used in LED lighting applications.
- It is used in wave shaping circuits in radar, computers, and other electronic devices.
Facts
Strength of magnetic field in a current carrying conductor
Strength of magnetic field in a current-carrying conductor When an electric current is passed through a conductor a magnetic field is produ...
-
Charging of a capacitor A capacitor is one of the electric components of an electrical circuit or network. A capacitor is a storing device...
-
Self-inductance of a solenoid Self-inductance is a process of induction of emf or voltage in a winding. A coil induces emf when the magne...
-
How does an electric motor work What is an electric motor? Electric motors are the fundamental part of doing any machinery work. No machine ...